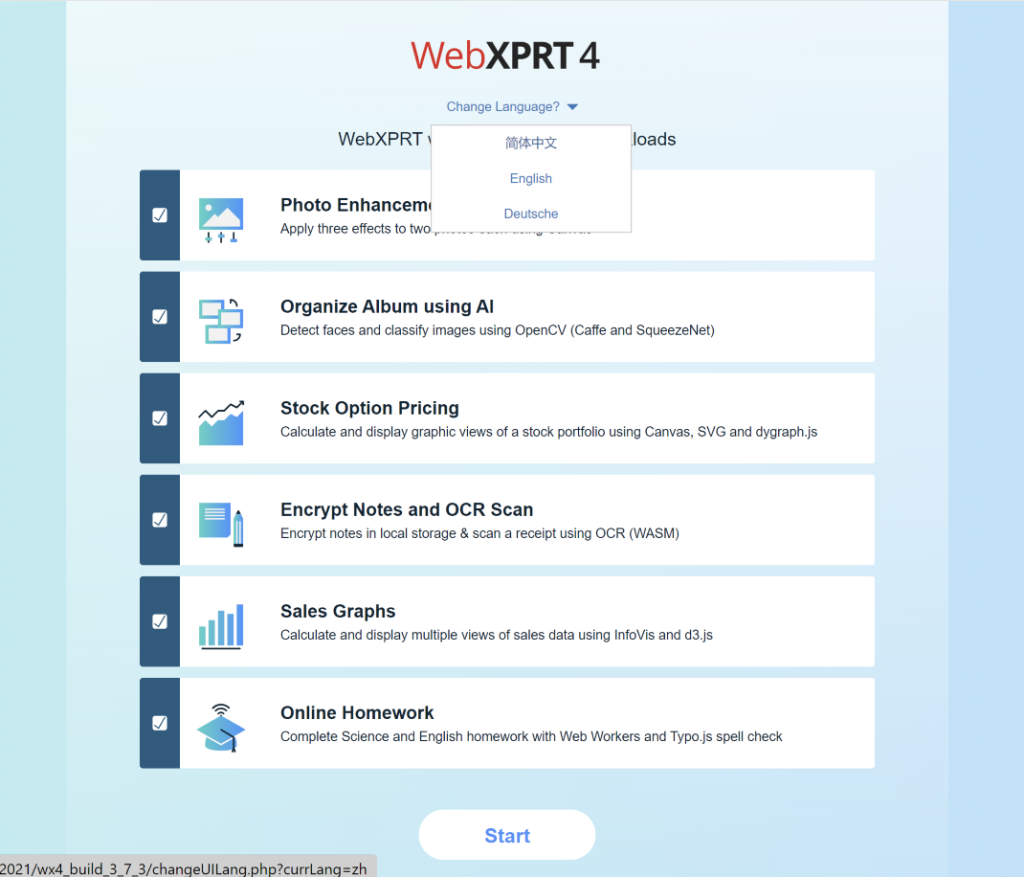
Recently, we announced that we’re moving forward with the development of a new AI-focused WebXPRT 4 workload. It will be an auxiliary workload, which means that it will run as a separate, optional test, and it won’t affect existing WebXPRT 4 tests or scores. Although the inspiration for this new workload came from internal WebXPRT discussions—and, let’s face it, from the huge increase in importance of AI—we wanted to remind you that we’re always open to hearing your WebXPRT workload ideas. If you’d like to submit proposals for new workloads, you don’t have to follow a formal process. Just contact us, and we’ll start the conversation.
If
you do decide to send us a workload proposal, it will be helpful to know the
types of parameters that we keep in mind. Below, we discuss some of the key
questions we ask when we evaluate new WebXPRT workload ideas.
Will
it be relevant and interesting to real users, lab testers, and tech reviewers?
When
considering a WebXPRT workload proposal, the first two criteria are simple: is
it relevant in real life, and are people interested in the workload? We created
WebXPRT to evaluate device performance using web-based tasks that consumers are
likely to experience daily, so real-life relevance has always been an essential
requirement for us throughout development. There are many technologies,
functions, and use cases that we could test in a web environment, but only some
are relevant to common applications or usage patterns and are likely to draw
the interest of real users, lab testers, and technical reviewers.
Will
it have cross-platform support?
Currently,
WebXPRT runs on almost any web browser and almost every device that supports a
web browser. We would like to keep that level of cross-platform support when we
introduce new workloads. However, technical differences in how various browsers
execute tasks make it challenging to include certain scenarios without
undermining our cross-platform ideal. When considering any workload proposal,
one of the first questions we ask is, “Will it work on all the major browsers
and operating systems?”
There
are special exceptions to this guideline. For instance, we’re still in the
early days of browser-based AI, and it’s unlikely that a new browser-based AI
workload will run on every major browser. If it’s a particularly compelling
idea, such as the AI scenario we’re currently working on, we may consider
including it as an auxiliary test.
Will
it differentiate performance between different types of devices?
XPRT
benchmarks provide users with accurate measures for evaluating how well target
systems or technologies perform specific tasks. With a broadly targeted
benchmark like WebXPRT, if the workloads are so heavy that most devices can’t
handle them or so light that most devices complete them without being taxed,
the results will be of little use for helping buyers evaluating systems and
making purchasing decisions, OEM labs, and the tech press.
That’s
why, with any new WebXPRT workload, we look for a sweet spot with respect to
how computationally demanding it will be. We want it to run on a wide range of
devices—from low-end devices that are several years old to brand-new high-end
devices, and everything in between. We also want users to see a wide range of
workload scores and resulting overall scores that accurately reflect the
experiences those systems deliver, so they can easily grasp the different
performance capabilities of the devices under test.
Will
results be consistent and easily replicated?
Finally,
WebXPRT workloads should produce scores that consistently fall within an
acceptable margin of error and are easily replicated with additional testing or
comparable gear. Some web technologies are very sensitive to uncontrollable or
unpredictable variables, such as internet speed. A workload that measures one
of those technologies would be unlikely to produce results that are consistent
and easily replicated.
We
hope this post will be useful if you’re thinking about potential new workloads
that you’d like to see in WebXPRT. If you have any general thoughts about
browser performance testing or specific workload ideas that you’d like us to
consider, please let us know.
Justin