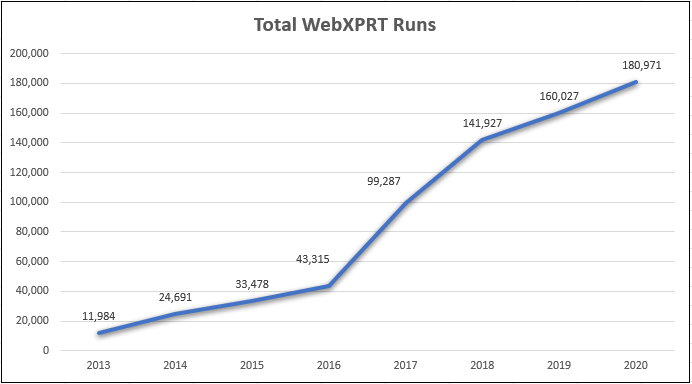
In early May, we sent a survey to members of the tech press who regularly use WebXPRT in articles and reviews. We asked for their thoughts on several aspects of WebXPRT, as well as what they’d like to see in the upcoming fourth version of the benchmark. We also published the survey questions here in the blog, and invited experienced WebXPRT testers to send their feedback as well. We received some good responses to the survey, and for the benefit of our readers, we’ve summarized some of the key comments and suggestions below.
- One respondent stated that WebXPRT is demanding enough to test performance, but if we want to simulate modern web usage, we should find the most up-to-date studies on common browser tasks and web technologies. This suggestion lines up with our intention to study the feasibility of adding a WebAssembly workload.
- One respondent liked that fact that unlike many other browser benchmarks, WebXPRT tests more than just JavaScript calculation speed.
- One respondent suggested that we include a link to a WebXPRT white paper within the UI, or at least a guide describing what happens during each workload.
- One respondent stated that they would like for WebXPRT to automatically produce a good result file on the local test system.
- One respondent said that WebXPRT has a relatively long runtime for a browser benchmark, and they would prefer that the runtime not increase in WebXPRT 4.
- We had no direct calls for a battery life test, because many testers already have scripts and/or methodologies in place for battery testing, but one tester suggested adding the ability to loop the test so users can measure performance over varying lengths of time.
- There were no requests to bring back any aspects of WebXPRT 2015 that we removed in WebXPRT 3.
- There were no reports of significant connection issues when testing with WebXPRT.
We greatly appreciate the members of the tech press that responded to the survey. We’re still in the planning stages of WebXPRT 4, so there’s still time for anyone to send comments or ideas to benchmarkxprtsupport@principledtechnologies.com. We look forward to hearing from you!
Justin