As 2022 gets underway, we want to take this opportunity to look back on 2021 and review another productive year for the XPRTs. Readers of our newsletter are familiar with the stats and updates we include each month, but for our blog readers who don’t receive the newsletter, we’ve compiled some highlights below.
Benchmarks
In the past year, we released the WebXPRT 4 Preview, CloudXPRT v1.1, and an updated CrXPRT 2 build that included a
fix for prior issues with the battery life test.
XPRTs in the media
Journalists, advertisers, and analysts referenced the XPRTs thousands of times in 2021. It’s always rewarding to know that the XPRTs have proven to be useful and reliable assessment tools for technology publications such as AnandTech, Expert Reviews, Gadgets 360, Gizmodo, Hot Hardware, Laptop Mag, Legit Reviews, Notebookcheck, PCMag, PCWorld, TechPowerUp, Tom’s Hardware, and ZDNet.
Downloads and confirmed runs
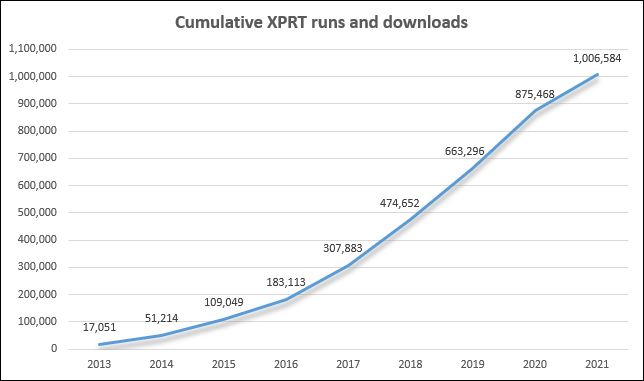
In 2021, we had more than 23,600 benchmark downloads and 228,900 confirmed runs. Our most popular benchmark, WebXPRT, just passed 909,800 runs since its debut in 2013! WebXPRT continues to be a go-to, industry-standard performance benchmark for OEM labs, vendors, and leading tech press outlets around the globe.
Media, publications, and interactive tools
Part of our mission with the XPRTs is to produce tools and materials that help testers better understand the ins and outs of benchmarking in general and the XPRTs in particular. To help achieve this goal, we published the following in 2021:
- the WebXPRT 4 Preview results viewer
- an interactive CloudXPRT learning tool
- the Overview of the CloudXPRT Data Analytics Workload white paper
- a new XPRTs around the world infographic
We’re thankful for everyone who has used the XPRTs, joined the community, and sent questions and suggestions throughout 2021. We look forward to an exciting 2022!
Justin